Salmobase

Updates
Update 2025-09-11
- Added assembly: Arctic charr (fSalAlp1.1)
Update 2025-04-11
- Gene expression plot added to gene page
Update 2023-04-11
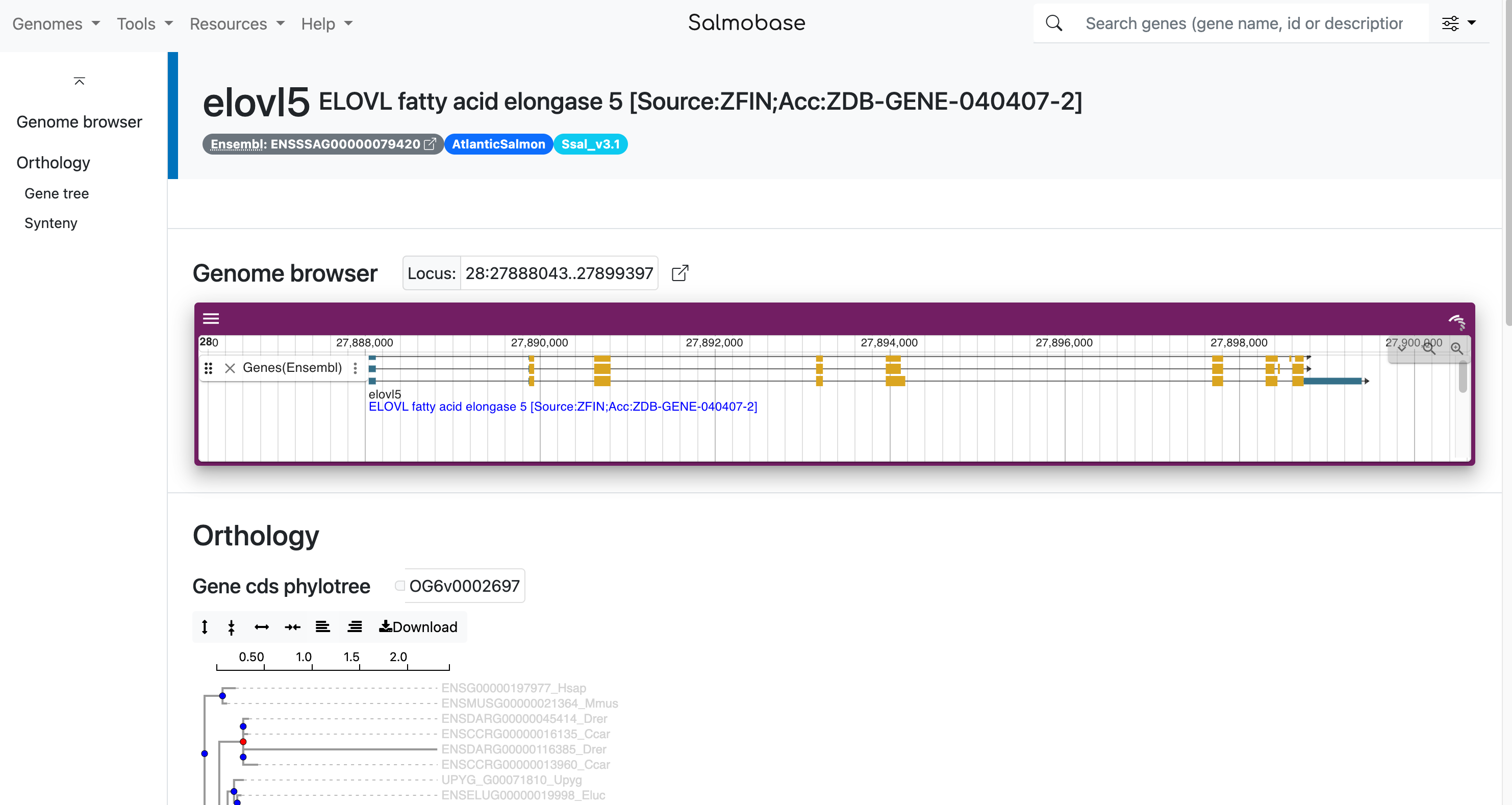
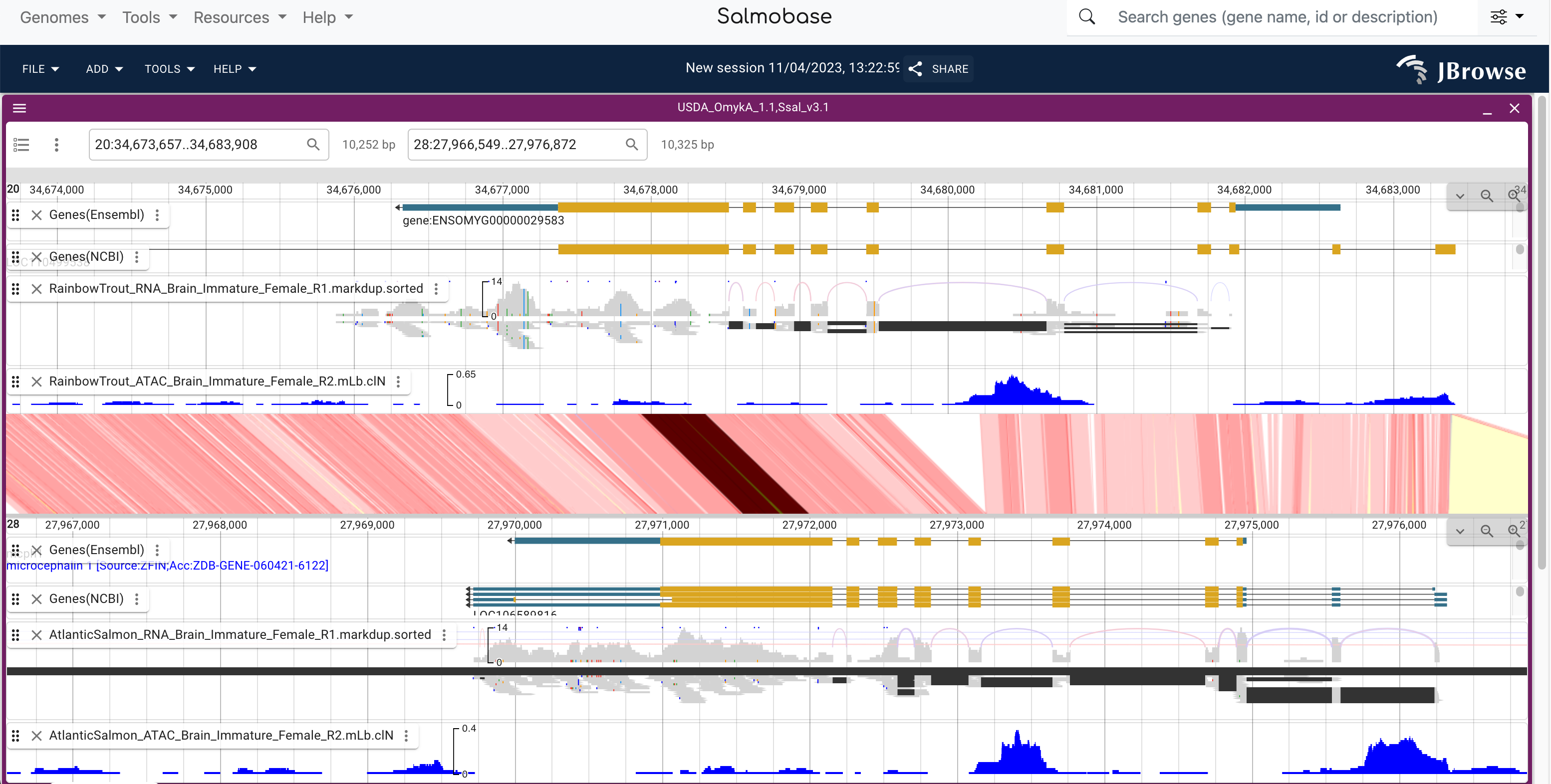
- "Genome browser" removed from menu. The genome browser can now be opened from the genome page by clicking on a chromosome or by select JBrowse from the tools menu.
- Link to download choromosomes.tsv on genome page.
- Added tracks:
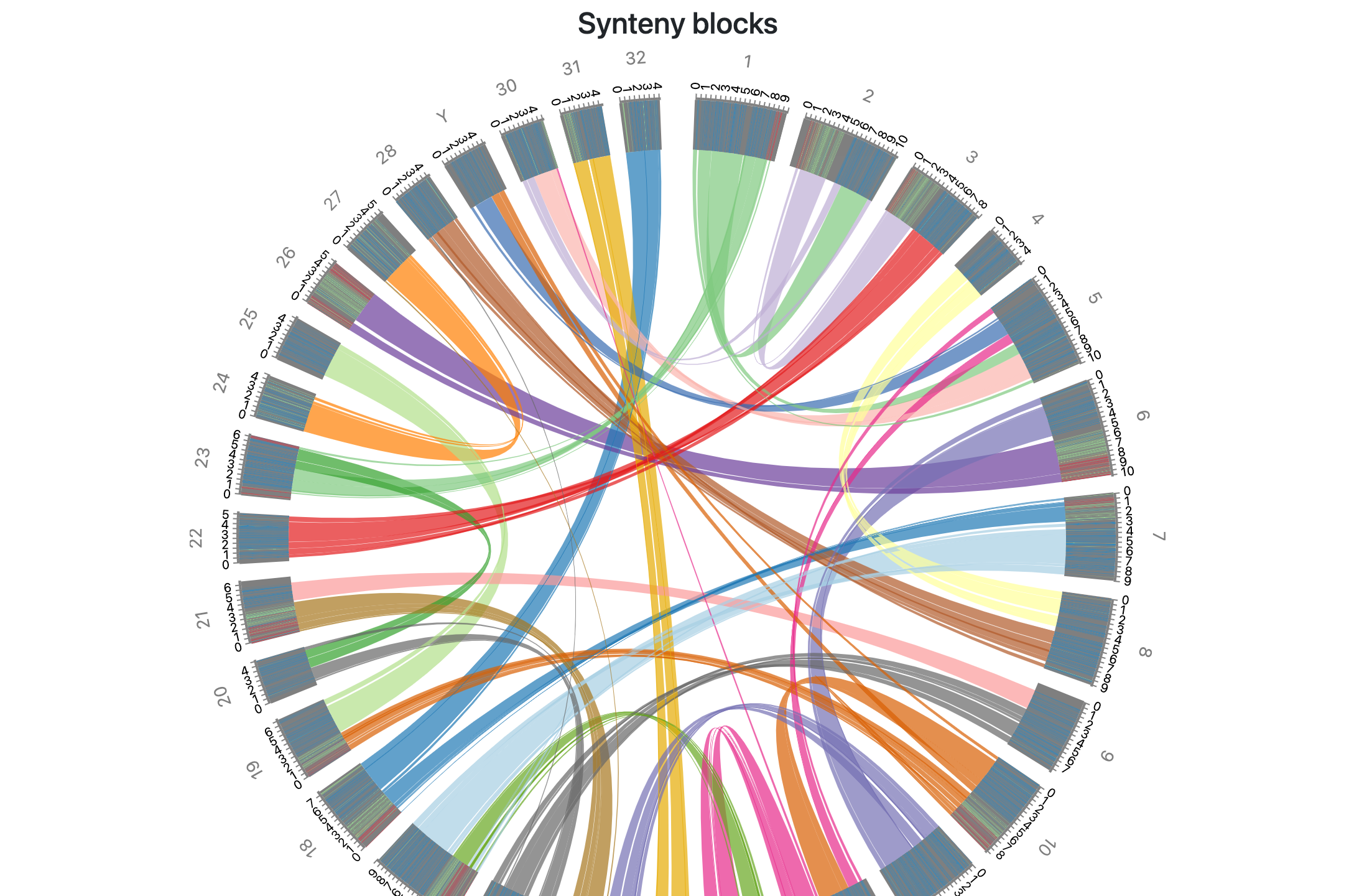
- Comparative genome alignments for salmon and trout
- Comparative ortholog/paralog tracks
Update 2023-01-02:
- Added assemblies:
- Atlantic salmon: Ssal_Brian_v1.0
- Atlantic salmon: Ssal_ALTA
- Gene page now shows link between Ensembl and NCBI annotation
Correction 2022-12-05:
The assembly that was originally submitted as Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) has been corrected to Dolly Varden (Salvelinus malma). See this retraction notice.November 2022 Update:
- Added assemblies:
- Atlantic salmon: Ssal_v3.1
- Rainbow trout: USDA_OmykA_1.1
- Coho salmon: Okis_V2
- Now includes both NCBI and Ensembl annotations when available.
- Support for multiple assemblies per species (I.e. old assemblies are still available).
- Added filter for gene search: Search selected species, assembly or annotation.
- New gene trees and ortholog groups for the new species based on Ensembl annotations.
- Chromosome alias: Now possible to load tracks with alternative sequence names. Valid sequence IDs are. refseq, genbank, Ensembl or “sequence name”. Aliases are also displayed when hovering the chromosome on the genome page.
- Gene page URL now uses geneIDs by default (NCBI gene ID or Ensembl gene ID). Gene annotations from earlier assemblies can be accessed by specifying the assembly with a parameter. E.g. https://salmobase.org/genes/id/100306804?assembly=ICSASG_v2
About Salmobase
Salmobase is a tool for making molecular genomic resources for salmonid species publically available in a framework of visualizations and analytic tools.
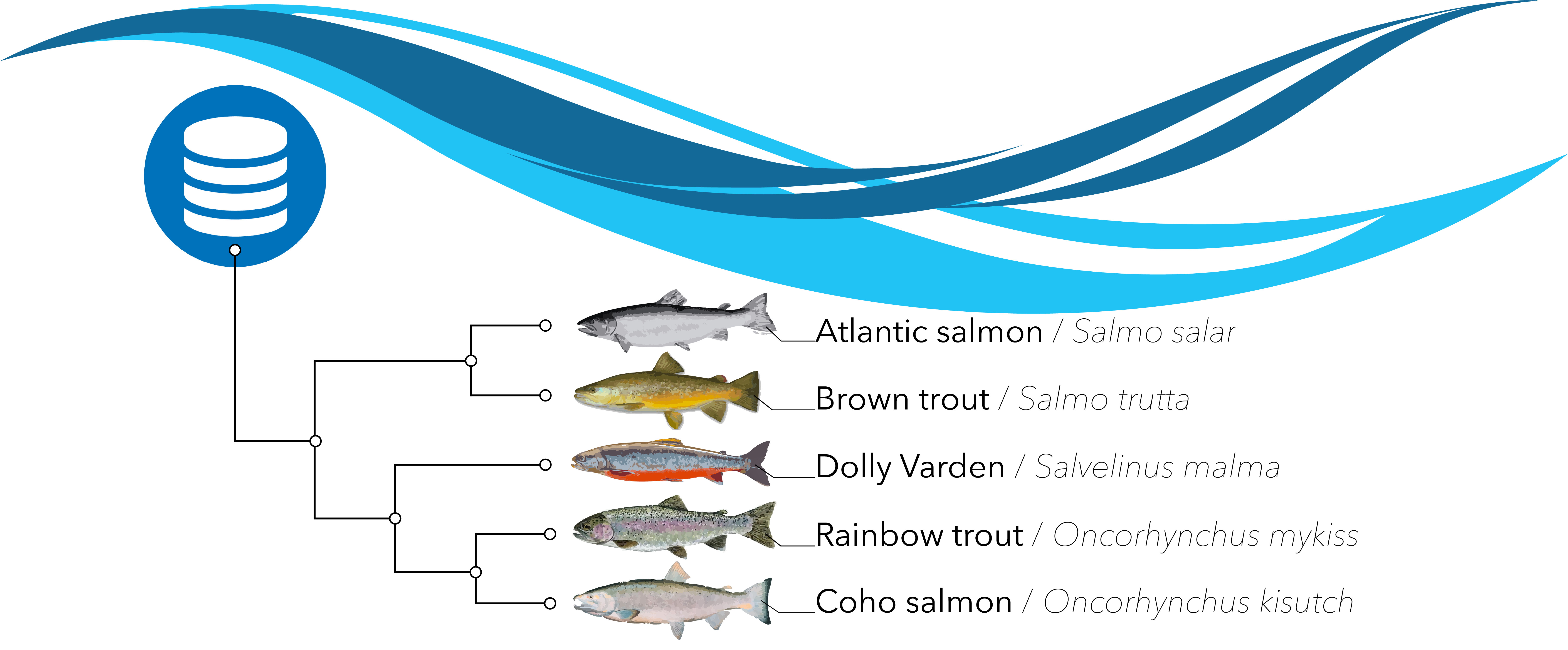
Salmonids are ray-finned fishes which constitute 11 genera and at least 70 species including Atlantic salmon, whitefishes, graylings, rainbow trout, and char.
The common ancestor of all Salmonidae experienced a whole genome duplication (WGD) ~80 million years ago, resulting in an autotetraploid genome.
Genomic rediplodization is still going on in salmonid species, providing an unique system for studying evolutionary consequences of whole genome duplication.
In recent years, high quality genome sequences of Atlantic salmon and Rainbow trout has been established, due to their scientific and commercial values.
Feedback
We appreciate your feedback! Please report any issues with the site or suggest a new feature or dataset you would like to see here by sending an e-mail